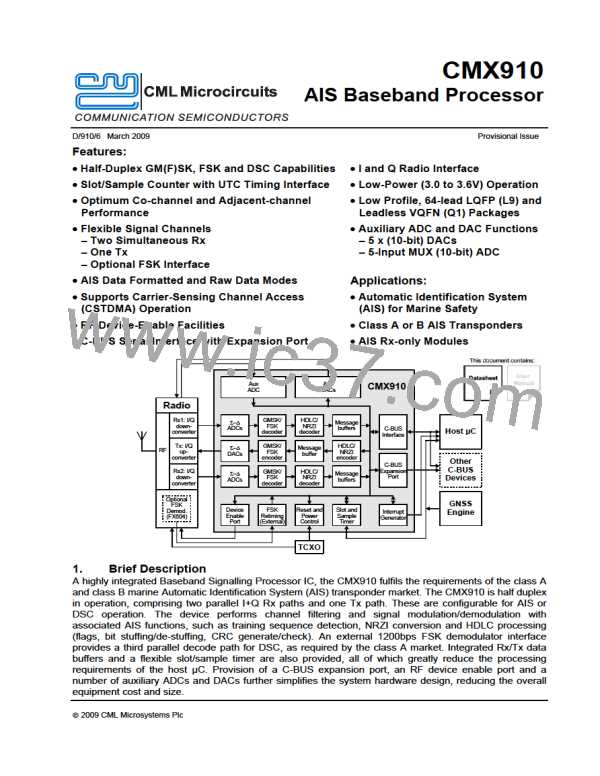
AIS Baseband Processor
CMX910
Tx State Reset
Idle
Tx Start
issued
Tx
Tx Start reissued
pending
Start point reached
CSTDMA active,
carrier sensed
Tx Done interrupt
Tx complete,
Tx FIFO not empty
Chained
message
Tx in
progress
Tx abort,
carrier
sensed
Tx complete,
Tx FIFO empty
Tx Done interrupt
Figure 7 Tx (AIS raw mode) state transitions
5.5.3 AIS Burst Mode Transmit
In AIS burst mode, an entire message is transferred to the CMX910 prior to transmission. The CMX910
then processes the data by performing bit stuffing, NRZI encoding and addition of training sequence,
start/stop flags and CRC checksum as required by AIS. The resulting bit stream is held in a secondary
message buffer within the CMX910. This message processing must be complete before transmission is
allowed to begin, so it is not possible to get a Tx underflow error in AIS burst mode. Note: in AIS burst
mode, the data bytes are automatically transmitted least significant bit first as required by the AIS
specification.
The µC is expected to perform the following sequence of operations in order to transmit an AIS data
packet in burst mode:
•
•
Initialise the transmitter timing registers as described in section 5.5.5. (This only needs to be done
once after the device has come out of reset).
Check that the Tx State flags in the Tx_Status register indicate that the transmitter is in the Idle
state and that Tx_FIFO does not contain data from an earlier aborted transmission. If necessary,
the transmitter state machine can be reset and Tx_FIFO can be cleared by writing 1 to Tx_Control
register b1-0.
•
Write the total number of data bits to be transmitted into the Tx_Bits register. This should be the
number of data bits in the packet excluding any bit stuffing bits, flags, CRC checksum or training
sequence. The AIS specification requires this number to be a multiple of eight.
Load the whole (up to 5 slot) message into the CMX910 through Tx_FIFO.
Write the timing reference slot number to Tx_Slot (this will most likely be a one or two slots before
the slot in which to transmit data, to allow time for the external Tx circuits to power up).
Request a transmission by writing to the Tx Start bit in the Tx_Control register.
Wait for a Tx Done interrupt, then check the transmitter state in the Tx_Status register to
determine if the transmission was successful.
•
•
•
•
© 2009 CML Microsystems Plc
25
D/910/6
 CMLMICRO [ CML MICROCIRCUITS ]
CMLMICRO [ CML MICROCIRCUITS ]