MT91L60
Advance Information
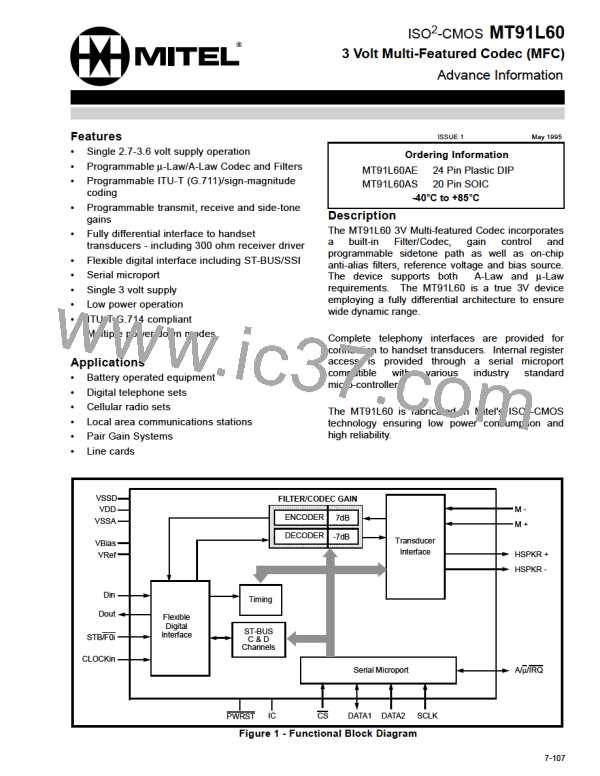
Microport
these two schemes for normal data bytes. However,
to ensure
decoding of the R/W and address
information, the Command/Address byte is defined
differently for Intel operation than it is for Motorola/
National operation. Refer to the relative timing
diagrams of Figures 5 and 6.
The serial microport, compatible with Intel MCS-51
(mode 0), Motorola SPI (CPOL=0,CPHA=0) and
National Semiconductor Microwire specifications
provides access to all MT91L60 internal read and
write registers. This microport consists of a transmit/
receive data pin (DATA1), a receive data pin
(DATA2), a chip select pin (CS) and a synchronous
data clock pin (SCLK). For D-channel contention
control, in ST-BUS mode, this interface provides an
open-drain interrupt output (IRQ).
Receive data is sampled on the rising edge of SCLK
while transmit data is made available concurrent with
the falling edge of SCLK.
Flexible Digital Interface
The microport dynamically senses the state of the
serial clock (SCLK) each time chip select becomes
active. The device then automatically adjusts its
internal timing and pin configuration to conform to
Intel or Motorola/National requirements. If SCLK is
high during chip select activation then Intel mode 0
timing is assumed. The DATA1 pin is defined as a
bi-directional (transmit/receive) serial port and
DATA2 is internally disconnected. If SCLK is low
during chip select activation then Motorola/National
timing is assumed. Motorola processor mode
CPOL=0, CPHA=0 must be used. DATA1 is defined
as the data transmit pin while DATA2 becomes the
data receive pin. Although the dual port Motorola
controller configuration usually supports full-duplex
communication, only half-duplex communication is
possible in the MT91L60. The micro must discard
non-valid data which it clocks in during a valid write
transfer to the MT91L60. During a valid read transfer
from the MT91L60 data simultaneously clocked out
by the micro is ignored by the MT91L60.
A serial link is required to transport data between the
MT91L60 and an external digital transmission
device. The MT91L60 utilizes the ST-BUS
architecture defined by Mitel Semiconductor but also
supports a strobed data interface found on many
standard Codec devices. This interface is commonly
referred to as Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI).
The combination of ST-BUS and SSI provides a
Flexible Digital Interface (FDI) capable of supporting
all Mitel basic rate transmission devices as well as
many other 2B+D transceivers.
The required mode of operation is selected via the
CSL2-0 control bits (Control Register 2, address
04h). Pin definitions alter dependent upon the
operational mode selected, as described in the
following subsections as well as in the Pin
Description tables.
Quiet Code
All data transfers through the microport are two-byte
transfers requiring the transmission of a Command/
Address byte followed by the data byte written or
read from the addressed register. CS must remain
asserted for the duration of this two-byte transfer. As
shown in Figures 5 and 6 the falling edge of CS
indicates to the MT91L60 that a microport transfer is
about to begin. The first 8 clock cycles of SCLK after
the falling edge of CS are always used to receive the
Command/Address byte from the microcontroller.
The Command/Address byte contains information
detailing whether the second byte transfer will be a
read or a write operation and at what address. The
next 8 clock cycles are used to transfer the data byte
between the MT91L60 and the microcontroller. At the
end of the two-byte transfer CS is brought high again
to terminate the session. The rising edge of CS will
tri-state the output driver of DATA1 which will remain
tri-stated as long as CS is high.
The FDI can be made to send quiet code to the
decoder and receive filter path by setting the RxMute
bit high. Likewise, the FDI will send quiet code in the
transmit path when the TxMute bit is high. Both of
these control bits reside in Control Register 1 at
address 03h. When either of these bits are low their
respective paths function normally. The -Zero entry
of Table 1 is used for the quiet code definition.
ST-BUS Mode
The ST-BUS consists of output (DSTo) and input
(DSTi) serial data streams, in FDI these are named
Dout and Din respectively, a synchronous clock input
signal CLOCKin (C4i), and a framing pulse input
(F0i). These signals are direct connections to the
corresponding pins of Mitel basic rate devices. The
CSL2, CSL1 and CSL0 bits are set to 1 for ST-BUS
operation.
Intel processors utilize least significant bit first
transmission while Motorola/National processors
employ most significant bit first transmission. The
MT91L60 microport automatically accommodates
7-112
 MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]
MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]