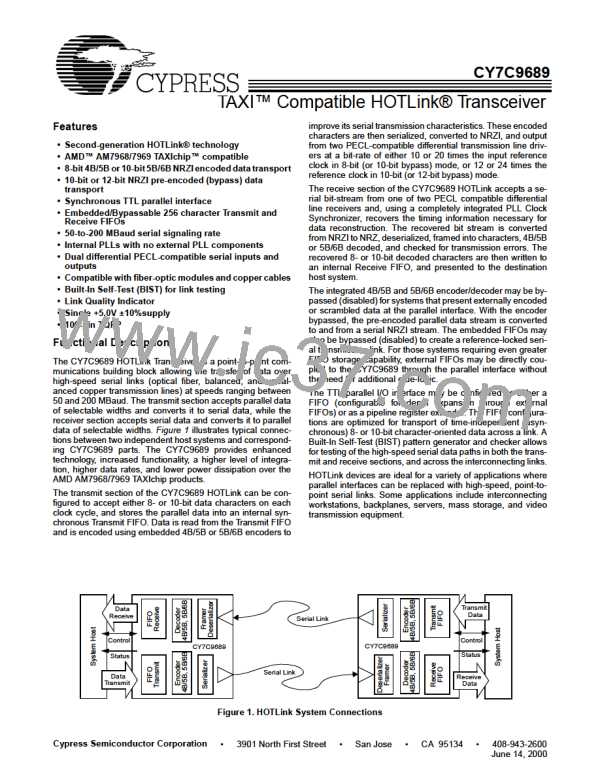
CY7C9689
Transmit FIFO Reset Sequence
TXCLK
The Transmit FIFO reset sequence (see Figure 13) is started
when TXRST and CE are first sampled LOW by the rising edge
of TXCLK. Because a Tx_RstMatch condition is present, the
Transmit FIFO flags are asserted and can be used to track the
status of any Transmit FIFO reset in progress. Once the reset
sequence has reached its maximum count (eight TXCLK cy-
cles), the Transmit FIFO flags are asserted to indicate a FULL
condition (TXEMPTY is deasserted, and both TXHALF and
TXFULL are asserted). This indicates that the Transmit FIFO
reset has been recognized by the Transmit Control State Ma-
chine and that a reset has been started. However, if the TXEN
is asserted prior to or during the assertion and sampling of
TXRST, the reset sequence is inhibited until TXEN is removed.
TXRST
CE
[46]
[46]
Tx_RstMatch
Tx_Match
TXFULL
Va lid
NOTE:
The FIFO FULL state forced by the reset operation is
different from a FULL state caused by normal FIFO data
writes. For normal FIFO write operations, when FULL is first
asserted, the Transmit FIFO must still accept up to four addi-
tional writes of data. When a FULL state is asserted due to a
Transmit FIFO reset operation, the FIFO will not accept any
additional data.
Figure 11. Transmit FIFO Reset Address Match
RXCLK
RXRST
The Transmit FIFO reset does not complete until the external
reset condition is removed. This can be removed by deasser-
tion of either TXRST or CE. If CE is deasserted (HIGH) to
remove the reset condition, the Transmit FIFO flag’s drivers are
disabled, and the Transmit FIFO must be addressed at a later
time to validate completion of the Transmit FIFO reset. If
TXRST is deasserted (HIGH) to remove the reset condition,
the Tx_RstMatch is changed to a Tx_Match, and the Transmit
FIFO status flags remain driven. The Transmit FIFO reset op-
eration is complete when the Transmit FIFO flags indicate an
EMPTY state (TXEMPTY is asserted and both TXHALF and
TXFULL are deasserted). A valid Transmit FIFO reset se-
quence is shown in Figure 13.
CE
[46]
Rx_RstMatch
[46]
Rx_Match
RXEMPTY
Valid Valid
Figure 12. Receive FIFO Reset Address Match
Here the TXRST and CE are asserted (LOW) at the same
time. When these signals are both sampled LOW by TXCLK,
a Tx_RstMatch condition is present. With TXEN deasserted
(HIGH), the Transmit FIFO is not selected for data transfers.
This Tx_RstMatch condition must remain for eight TXCLK cy-
cles to initiate the Tx_FIFO_Reset. Following this the TXFULL
FIFO status flag is asserted to indicate that the Transmit FIFO
reset sequence has completed and that a Transmit FIFO reset
is in progress.
CLK. When an Rx_RstMatch (or Rx_Match) condition is
present, the RXEMPTY and RXFULL output drivers are en-
abled. When an Rx_RstMatch (or Rx_Match) condition is not
present, these same drivers are disabled (High-Z). The Re-
ceive FIFO reset Address Match is shown in Figure 12. Note
that while the FIFO flags remain asserted for more than one
clock cycle, this is due to an Rx_Match condition, not a contin-
uation of the Rx_RstMatch.
When the TXRST signal is deasserted (HIGH), CE remains
LOW to allow the FIFO status flags to be driven. This allows
the completion of the reset operation to be monitored. To allow
better multi-tasking on multi-PHY implementations, it is possi-
ble to deassert CE (HIGH) as soon as the FULL state is indi-
cated. The FIFO reset operation will complete and the EMPTY
state (indicating completion of the reset operation) can be de-
tected during a separate polling operation.
FIFO Reset Sequence
On power-up, the Transmitter and Receiver FIFOs are cleared
automatically. If the usage of the FIFOs in specific operating
modes results in stale or unwanted data, this data can be
cleared by resetting the respective FIFO. Data in the Transmit
FIFO will empty automatically if it is enabled to read the FIFO
(assuming TXHALT is not LOW). Stale received data can be
“flushed” by reading it, or the Receive FIFO can be reset to
remove the unwanted data.
For those links implemented with a single PHY, it is possible to
hardwire CE LOW and still perform normal accesses and reset
operations. This is shown in Figure 14. In a single-PHY imple-
mentation, a Transmit FIFO reset can never be initiated with
TXEN asserted at the same time as TXRST. Since CE is
always LOW, any assertion of TXEN causes the Transmit FIFO
to be selected, clearing the reset counter.
The Transmit and Receive FIFOs are reset when the
Tx_RstMatch or Rx_RstMatch condition remains present for
eight consecutive clock cycles. Any disruption of the reset se-
quence prior to reaching the eight cycle count, either by re-
moval of CE or the respective TXRST or RXRST, or assertion
of the associated TXEN or RXEN, terminates the sequence
and does not reset the FIFO. Because CE must remain assert-
ed during the reset sequence, the addressed FIFO flags re-
main driven during the entire sequence.
Figure 15 shows a sequence of input signals which will not
produce a FIFO reset. In this case TXEN was asserted to se-
lect a Transmit FIFO for data transfers. Because TXEN re-
mains active, the assertion of CE and TXRST does not initiate
43
 CYPRESS [ CYPRESS ]
CYPRESS [ CYPRESS ]