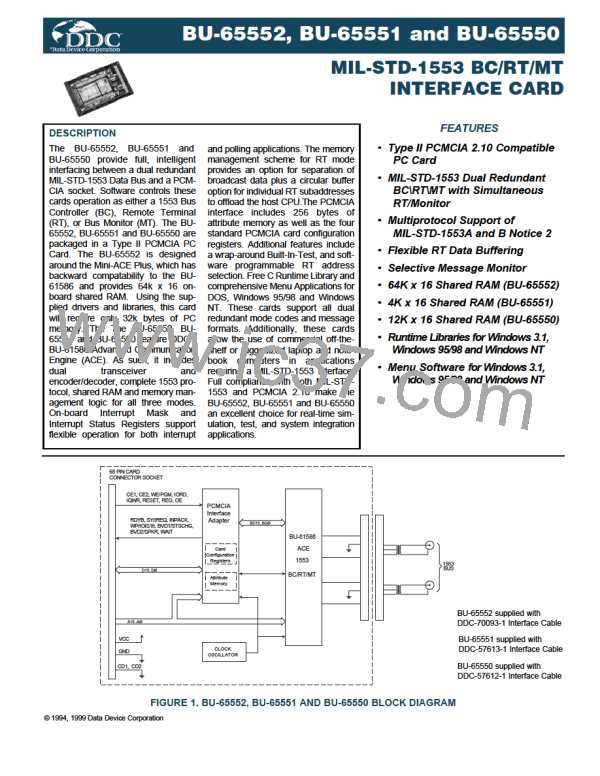
DESCRIPTOR STACK
Commands may be illegalized down to the word count level. For
example, a one-word receive command to subaddress 1 may be
legal, while a two-word receive command to subaddress 1 may
be illegalized.
At the beginning and end of each message, the BU-65552, BU-
65551 and BU-65550 RT stores a four-word message descriptor
in the active area stack. The RT stack size is programmable,
with choices of 256, 512, 1024, and 2048 words. FIGURES 5, 6
and 7 show the four words: Block Status Word, Time Tag Word,
Data Block Pointer, and the 1553 received Command Word. The
RT Block Status Word includes indications of message in-
progress or message complete, bus channel, RT-to-RT transfer
and RT-to-RT transfer errors, message format error, loop test
(self-test) failure, circular buffer rollover, illegal command, and
other error conditions. TABLE 23 shows the bit mapping of the
RT Block Status Word.
The first 64 words of the Illegalization Table refer to broadcast
receive commands (two words per subaddress). The next 64
words refer to broadcast transmit commands. Since nonmode
code broadcast transmit commands are by definition invalid, this
section of the table (except for subaddresses 0 and 31) does not
need to be initialized by the user. The next 64 words correspond
to nonbroadcast receive commands. The final 64 words refer to
nonbroadcast transmit commands. Messages with Word Count/
Mode Code (WC/MC) fields between 0 and 15 may be illegalized
by setting the corresponding data bits for the respective even-
numbered address locations in the illegalization table. Likewise,
messages with WC/MC fields between 16 and 31 may be ille-
galized by setting the corresponding data bits for the respective
odd-numbered address locations in the illegalization table.
As in BC mode, the Time Tag Word stores the current contents
of the BU-65552, BU-65551 and BU-65550 read/writable Time
Tag Register. The resolution of the Time Tag Register is pro-
grammable from among 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 µs/LSB. Also,
incrementing of the Time Tag counter may be from an external
clock source or via software command.
The following should be noted with regards to command illegal-
ization:
The ACE stores the contents of the accessed Lookup Table
location for the current message, indicating the starting location
of the Data Word block, as the Data Block Pointer. This serves
as a convenience in locating stored message data blocks. The
ACE stores the full 16-bit 1553 Command Word in the fourth
location of the RT message descriptor.
(1)To illegalize a particular word count for a given broad-
T/R
cast/own address-
subaddress, the appropriate bit posi-
tion in the respective illegalization word should be set to logic
1. A bit value of logic 0 designates the respective Command
Word as a egal command. The BU-65552, BU-65551 and
BU-65550 will respond to an illegalized non-broadcast com-
mand with the Message Error bit set in its RT Status Word.
RT COMMAND ILLEGALIZATION
The BU-65552, BU-65551 and BU-65550 provide an internal
mechanism for RT command illegalization. In addition, there is a
means for allowing the setting of the Busy Status Word bit to be
only for a programmed subset of the transmit/receive/broadcast
subaddresses.
(2)For subaddresses 00001 through 11110, the "WC/MC"
field specifies the Word Count field of the respective
Command Word. For subaddresses 00000 and 11111, the
TABLE 30. ILLEGALIZATION RAM ADDRESS DEFINITION
DESCRIPTION
The illegalization scheme uses a 256-word area in the shared
RAM address space. A benefit of this feature is the reduction of
printed circuit board requirements, by eliminating the need for an
external PROM, PLD, or RAM device that does the illegalizing
function. The BU-65552, BU-65551 and BU-65550 illegalization
scheme provides maximum flexibility, allowing any subset of the
BIT
0
15 (MSB)
14
13
12
11
10
9
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
T/R
4096 possible combinations of broadcast/own address,
bit,
subaddress, and word count/mode code to be illegalized.
Another advantage of the RAM-based illegalization technique is
that it provides for a high degree of self-test ability.
Addressing The Illegalization Table
8
TABLE 30 illustrates the addressing scheme of the illegalization
RAM . As shown, the base address of the illegalizing RAM is
word address 0300 (hex) in the shared RAM. The ACE formu-
lates the index into the Illegalizing Table based on the values of
7
BROADCAST/OWNADDRESS
6
T/R
5
SA4
T/R
BROADCAST/OWN ADDRESS,
bit, Subaddress, and the
4
SA3
MSB of the Word Count/Mode Code field (WC/MC4) of the cur-
rent Command Word.
3
SA2
2
SA1
The internal RAM has 256 words reserved for command illegal-
ization. Broadcast commands may be illegalized separately from
non-broadcast receive commands and mode commands.
1
SA0
0 (LSB)
WC4/MC4
22
 ETC [ ETC ]
ETC [ ETC ]