TPS51640A, TPS59640, TPS59641
SLUSAQ2 –JANUARY 2012
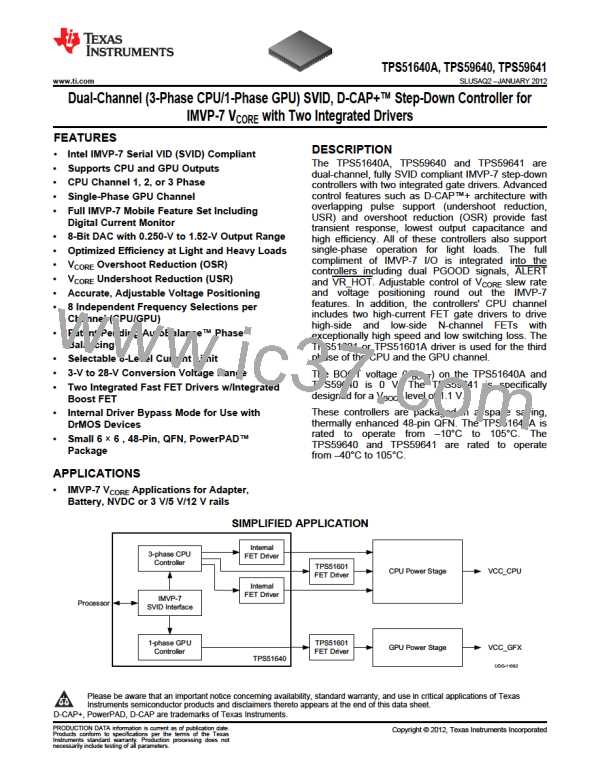
www.ti.com
AutoBalance™ Current Sharing
The basic mechanism for current sharing is to sense the average phase current, then adjust the pulse width of
each phase to equalize the current in each phase. (See Figure 69.)
The PWM comparator (not shown) starts a pulse when the feedback voltage meets the reference. The VBAT
voltage charges Ct(ON) through Rt(ON). The pulse is terminated when the voltage at Ct(ON) matches the t(ON)
reference, normally the DAC voltage (VDAC).
The circuit operates in the following fashion, using Figure 69 as the block diagram. First assume that the 5-µs
averaged value of I1 = I2 = I3. In this case, the PWM modulator terminates at VDAC, and the normal pulse width
is delivered to the system. If instead, I1 > IAVG, then an offset is subtracted from VDAC, and the pulse width for
Phase 1 is shortened, reducing the current in Phase 1 to compensate. If I1 < IAVG, then a longer pulse is
produced, again compensating on a pulse-by-pulse basis.
VBAT 37
RT(on)
VDAC
CCSP1
CCSN1
4
5
K x (I1-IAVG
)
)
)
+
PWM1
PWM2
PWM3
+
+
+
5 ms
Filter
+
Current
Amplifier
CT(on)
IAVG
RT(on)
VDAC
+
CCSP2
CCSN2
7
6
K x (I2-IAVG
5 ms
Filter
+
Current
Amplifier
CT(on)
IAVG
Averaging
Circuit
IAVG
RT(on)
VDAC
+
CCSP3
CCSN3
8
9
K x (I3-IAVG
5 ms
Filter
+
Current
Amplifier
CT(on)
IAVG
UDG-11036
Figure 69. Schematic Representation of AutoBalance Current Sharing
Dynamic VID and Power-State Changes
In IMVP-7, there are 3 basic types of VID changes:
•
•
•
SetVID-Fast
SetVID-Slow
SetVID-Decay
SetVID-Fast change and a SetVID-Slow change automatically puts the power state in PS0. A SetVID-Decay
change automatically puts the power state in PS2.
32
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]
TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]