MT9092
The ability to generate tones locally provides the
designer with a familiar method of feedback to the
telephone user as they proceed to set-up, and
ultimately, dismantle a telephone conversation. Also,
as the network slowly evolves from the dial pulse/
DTMF methods to the D-Channel protocols it is
essential that the older methods be available for
backward compatibility. As an example; once a call
has been established, say from your office to your
home, using the D-Channel signalling protocol it may
be necessary to use in-band DTMF signalling to
manipulate your personal answering machine in
order to retrieve messages. Thus the locally
generated tones must be of network quality and not
just a reasonable facsimile. The HPhone-II DSP can
generate the required tone pairs as well as single
tones to accommodate any in-band signalling
requirement.
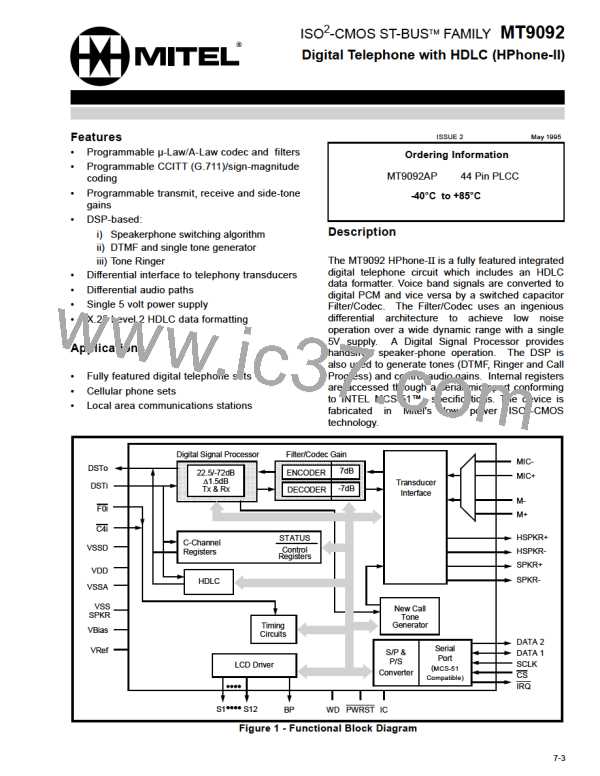
Overview
The functional block diagram of Figure 1 depicts the
main operations performed within the HPhone-II.
Each of these functional blocks will be described in
the sections to follow. This overview will describe
some of the end-user features which may be
implemented as a direct result of the level of
integration found within the HPhone-II.
The main feature required of a digital telephone is to
convert the digital Pulse Code Modulated (PCM)
information, being received by the telephone set, into
an analog electrical signal. This signal is then
applied to an appropriate audio transducer such that
the information is finally converted into intelligible
acoustic energy. The same is true of the reverse
direction where acoustic energy is converted first
into an electrical analog and then digitized (into
PCM) before being transmitted from the set. Along
the way if the signals can be manipulated, either in
the analog or the digital domains, other features
such as gain control, signal generation and filtering
may be added. More complex processing of the
digital signal is also possible and is limited only be
the processing power available. One example of this
processing power may be the inclusion of a complex
handsfree switching algorithm. Finally, most electro-
acoustic transducers (loudspeakers) require a large
amount of power to develop an effective acoustic
signal. The inclusion of audio amplifiers to provide
this power is required.
Each of the programmable parameters within the
functional blocks is accessed through a serial
microcontroller port compatible with Intel MCS-51
specifications.
Functional Description
In this section, each functional block within the
HPhone-II is described along with all of the
associated control/status bits. Each time a control/
status bit(s) is described it is followed by the address
register where it will be found. The reader is referred
to the section titled ‘Register Summary' for a
complete listing of all address map registers, the
control/status bits associated with each register and
a definition of the function of each control/status bit.
The Register Summary is useful for future reference
of control/status bits without the need to locate them
within the text of the functional descriptions.
The HPhone-II features Digital Signal Processing
(DSP) of the voice encoded PCM, complete Analog/
Digital and Digital/Analog conversion of audio
signals (Filter/CODEC) and an analog interface to
the external world of electro-acoustic devices
(Transducer Interface). These three functional blocks
combine to provide a standard full-duplex telephone
conversation utilizing a common handset. Selecting
transducers for handsfree operation, as well as
allowing the DSP to perform its handsfree switching
algorithm, is all that is required to convert the full-
duplex handset conversation into a half-duplex
speakerphone conversation. In each of these
modes, full programmability of the receive path and
side-tone gains is available to set comfortable
listening levels for the user as well as transmit path
gain control for setting nominal transmit levels into
the network.
Filter-CODEC
The Filter/CODEC block implements conversion of
the analog 3.3kHz speech signals to/from the digital
domain compatible with 64kb/s PCM B-Channels.
Selection of companding curves and digital code
assignment are register programmable. These are
CCITT G.711 A-law or µ-Law, with true-sign/
Alternate Digit Inversion or true-sign/Inverted
Magnitude coding, respectively. Optionally, sign-
magnitude coding may also be selected for
proprietary applications.
The HPhone-II’s HDLC block is easy to use in
proprietary signalling protocols such as those within
PABXs and Key Systems. A fully interrupt driven
interface, buffered by 19 byte FIFOs in each
The Filter/CODEC block also implements transmit
and receive audio path gains in the analog domain.
These gains are in addition to the digital gain pad
provided in the DSP section and provide an overall
path gain resolution of 0.5dB. A programmable gain,
direction,
simplifies
the
microcontroller's
asynchronous access to the D-Channel information.
7-6
 MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]
MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]