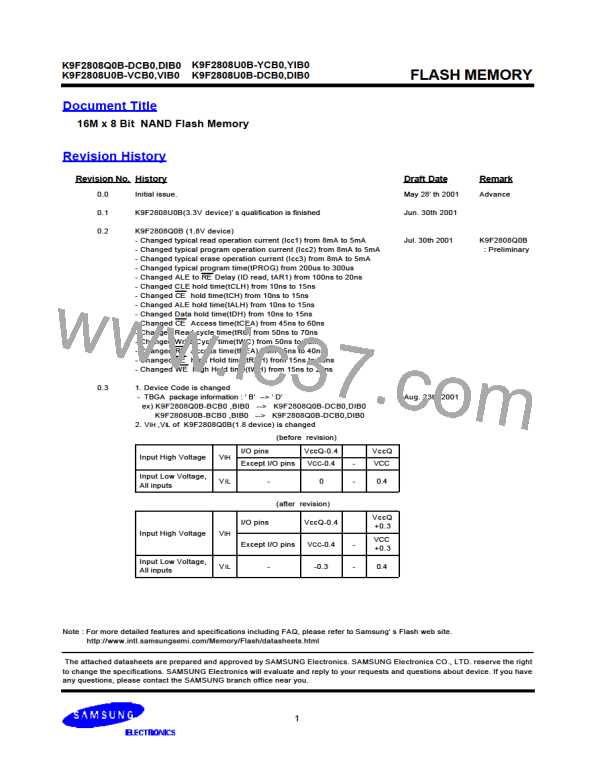
K9F2808U0B-YCB0,YIB0
K9F2808Q0B-DCB0,DIB0
K9F2808U0B-VCB0,VIB0 K9F2808U0B-DCB0,DIB0
FLASH MEMORY
BLOCK ERASE
The Erase operation is done on a block(16K Bytes) basis. Block Erase is executed by entering Erase Setup command(60h) and 2
cycle block addresses and Erase Confirm command(D0h). Only address A14 to A23 is valid while A9 to A13 is ignored. This two-
step sequence of setup followed by execution command ensures that memory contents are not accidentally erased due to external
noise condition. At the rising edge of WE after erase confirm command input, internal write controller handles erase and erase-veri-
fication. When the erase operation is completed, the Write Status Bit(I/O 0) may be checked.
Figure 10 details the sequence.
Figure 10. Block Erase Operation
tBERS
R/B
I/O0~7
Pass
60h
I/O0
Fail
Address Input(2Cycle)
Block Add. : A9 ~ A23
70h
D0h
READ STATUS
The device contains a Status Register which may be read to find out whether program or erase operation is completed, and whether
the program or erase operation is completed successfully. After writing 70h command to command register, a read cycle takes out
the content of the Status Register to the I/O pins on the falling edge of CE or RE. This two line control allows the system to poll the
progress of each device in multiple memory connections even when R/B pins are common-wired. RE or CE does not need to be tog-
gled for updated status. Refer to table 3 for specific Status Register definitions. The command register remains in Status Read mode
until further commands are issued to it. Therefore, if the status register is read during a random read cycle, a read command(00h or
50h) should be given before sequential page read cycle.
Table3. Read Status Register Definition
I/O #
Status
Definition
"0" : Successful Program / Erase
I/O 0
Program / Erase
"1" : Error in Program / Erase
I/O 1
I/O 2
I/O 3
I/O 4
I/O 5
I/O 6
I/O 7
"0"
"0"
"0"
"0"
"0"
Reserved for Future
Use
Device Operation
Write Protect
"0" : Busy
"1" : Ready
"1" : Not Protected
"0" : Protected
26
 SAMSUNG [ SAMSUNG ]
SAMSUNG [ SAMSUNG ]