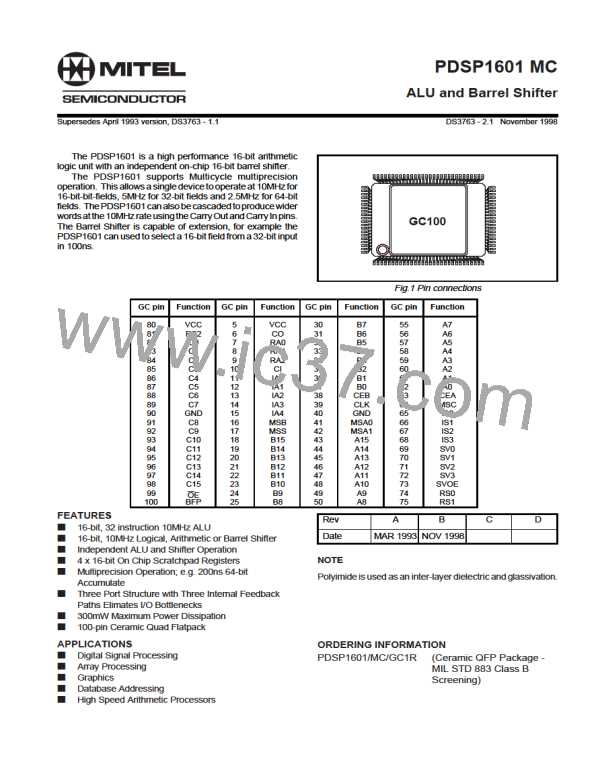
PDSP1601 MC
Divide by Two
The Barrel Shifter
The ALU has four (A2SGN, A2RAL, A2RAR, A2RSX)
instructions used for right shifting (dividing by two) extended
precision words. These words, (up to 64 bits) may be stored
in the two on-chip register files. When the least significant 16
bit word is shifted, the vacant MSB must be filled with the LSB
from the next most significant 16 bit byte. This is achieved via
the A2RAL, A2RAR or A2RSX instructions which indicate the
source of the new MSB (see SLU INSTRUCTION SET).
When the most significant 16 bit byte is right shifted, the
MSB must be filled with a duplicate of the original MSB so as
to maintain the correct sign (Sign Extension). This operation
is achieved via the A2SGN instruction (see Table 1).
The Barrel Shifter supports 16 instructions as detailed in
Table 2. The input to the Barrel Shifter is selected by the S
MUX. Data will fall through from the selected register, through
the S MUX and the Barrel Shifter to the shifter output register
file in 100ns.
The Barrel Shifter instructions are latched, such that the
instructions will not start executing until the rising edge of CLK
latches the instruction into the device.
TheBarrelShifteriscapableofLogicalArithmeticorBarrel
Shifts in either direction.
A. Logical shifts discard bits that exit the 16 bit field and fill
spaces with zeros.
Constants
B. Arithmetic shifts discard bits that exit the 16 bit field and
fill spaces with duplicates of the original MSB.
C. Barrel Shifts rotate the 16 bit fields such that bits tha exit
the 16 bit field to the left or right reappear in the vacant
spaces on the right or left.
The ALU has four instructions (OPONE, OPBYT, OPNIB,
OPALT) that force a constant value onto the ALU output.
These values are primarily intended to be used as masks, or
the seeds for mask generation, for example, the OPONE
instruction will set a single bit in the least significant position.
This bit may be rotated any where in the 16 bit field by the
BarrelShifter, allowingtheANDfunctionoftheALUtoperform
bit-pick operations on input data.
Theamountofshiftappliedisencodedontothe4bitBarrel
Shifter input as illustrated in Table 3. The type of shift and the
amount are determined by the shift control block. The shift
controlblock(seeFig.3)acceptsanddecodesthefourbitISO-
3 instruction. The shift control block contains a priority
encoder and two, user programmable 4 bit registers R1 and
R2.
CLR
The ALU instruction CLRXX is used as a Master Reset for
the entire device. This instruction has the effect of:
There are four possible sources of shift value that can be
passed onto the Barrel Shifter, there are:
1. Clearing ALU and Barrel Shifter register files to zero.
2. Clearing A and B port input registers to zero.
1. The Priority Encoder
2. The SV input
3. Clearing the R1 and R2 shift control registers to zero.
4. Clearing the internally registered CO bit to zero.
5. Programming the BFP flag to detect overflow conditions.
3. The R1 register
4. The R2 register
Mnemonic
Inst IS3-IS0
Operation
I/O
LSRSV
LSLSV
BSRSV
BSLSV
LSRR1
LSRR2
LSLR1
LSLR2
LR1SV
LR2SV
ASRSV
ASRR1
ASRR1
NRMXX
NRMR1
NRMR2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
Logical Shift Right by SV
Logical Shift Left by SV
Barrel Shift Right by SV
Barrel Shift Left by SV
I
I
I
I
X
X
X
X
I
Logical Shift Right by R1
Logical Shift Left by R1
Logical Shift Right by R2
Logical Shift Left by R2
Load Register 1 From SV
Load Register 2 From SV
Arithmetic Shift Right by SV
Arithmetic Shift Right by R1
Arithmetic Shift Right by R2
Normalise Output PE
I
I
X
X
O
O
O
Normalise Output PE, Load R1
Normalise Output PE, Load R2
Table 2 Barrel shifter instructions
MNEMONICS
LSXYY Logical Shift,
BSXYY Barrel Shift,
ASXYY Arithmetic Shift, X
LXXYY Load
NRMYY Normalise by PE, Output PE value on SV Port, Load YY Reg
KEY
SV
R1
R2
PE
I
X
X
= Direction YY = Source of Shift Value
= Direction YY = Source of Shift Value
= Direction YY = Source of Shift Value
= Shift Value
= Register 1
= Register 2
XX = Target YY = Source
= Priority Encoder Output
=> SV Port operates as an Input
=> SV Port operates as an Output
=> SV Port in a High Impedance State
O
X
5
 MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]
MITEL [ MITEL NETWORKS CORPORATION ]