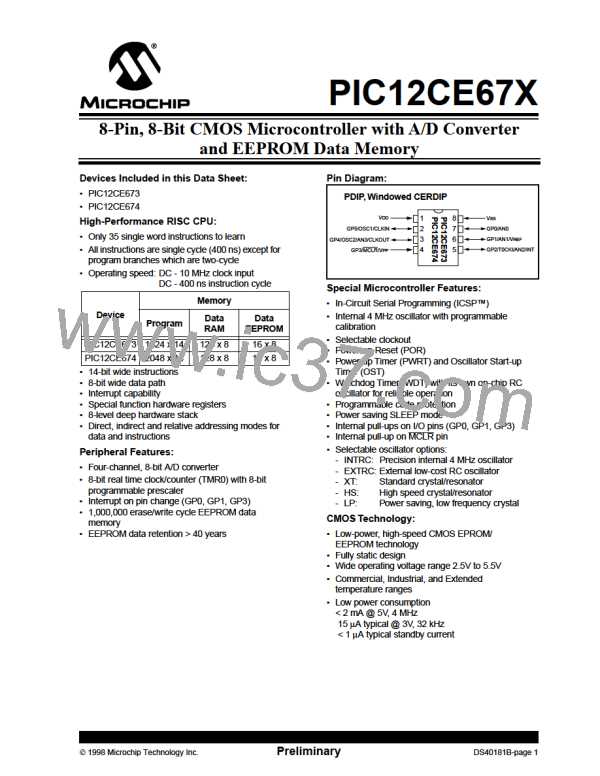
PIC12CE67X
4.3.2
STACK
4.3
PCL and PCLATH
The program counter (PC) is 13-bits wide.The low byte
comes from the PCL register, which is a readable and
writable register. The high byte (PC<12:8>) is not
directly readable or writable and comes from PCLATH.
On any reset, the PC is cleared. Figure 4-10 shows the
two situations for the loading of the PC. The upper
example in the figure shows how the PC is loaded on a
write to PCL (PCLATH<4:0> → PCH).The lower exam-
ple in the figure shows how the PC is loaded during a
CALLor GOTOinstruction (PCLATH<4:3> → PCH).
The PIC12C67X family has an 8 level deep x 13-bit
wide hardware stack. The stack space is not part of
either program or data space and the stack pointer is
not readable or writable. The PC is PUSHed onto the
stack when a CALLinstruction is executed or an inter-
rupt causes a branch. The stack is POPed in the event
of a RETURN, RETLWor a RETFIEinstruction execution.
PCLATH is not affected by a PUSH or POP operation.
The stack operates as a circular buffer.This means that
after the stack has been PUSHed eight times, the ninth
push overwrites the value that was stored from the first
push. The tenth push overwrites the second push (and
so on).
FIGURE 4-10: LOADING OF PC IN
DIFFERENT SITUATIONS
PCH
PCL
Note 1: There are no status bits to indicate stack
12
8
7
0
Instruction with
PCL as
overflow or stack underflow conditions.
PC
Destination
Note 2: There are no instructions/mnemonics
called PUSH or POP. These are actions
that occur from the execution of the CALL,
RETURN, RETLW, and RETFIE instruc-
tions, or the vectoring to an interrupt
address.
8
PCLATH<4:0>
PCLATH
5
ALU result
PCH
12 11 10
PCL
8
7
0
4.4
Program Memory Paging
GOTO, CALL
PC
The PIC12CE67X ignores both paging bits
PCLATH<4:3>, which are used to access program
memory when more than one page is available. The
use of PCLATH<4:3> as general purpose read/write
bits for the PIC12CE67X is not recommended since
this may affect upward compatibility with future prod-
ucts.
PCLATH<4:3>
PCLATH
11
2
Opcode <10:0>
4.3.1
COMPUTED GOTO
A computed GOTO is accomplished by adding an off-
set to the program counter (ADDWF PCL).When doing a
table read using a computed GOTO method, care
should be exercised if the table location crosses a PCL
memory boundary (each 256 byte block). Refer to the
application note “Implementing a Table Read" (AN556).
DS40181B-page 22
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
 MICROCHIP [ MICROCHIP ]
MICROCHIP [ MICROCHIP ]