FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
FUNCTIONAL DEVICE OPERATION
Single 5.0 V Supply, VIN1 = VIN2, or Dual Supply VIN1 ≠
1. VOUT falls faster than LDO. The LDO uses control
methods (1) and (2) described in the section Methods
of Control on page 22.
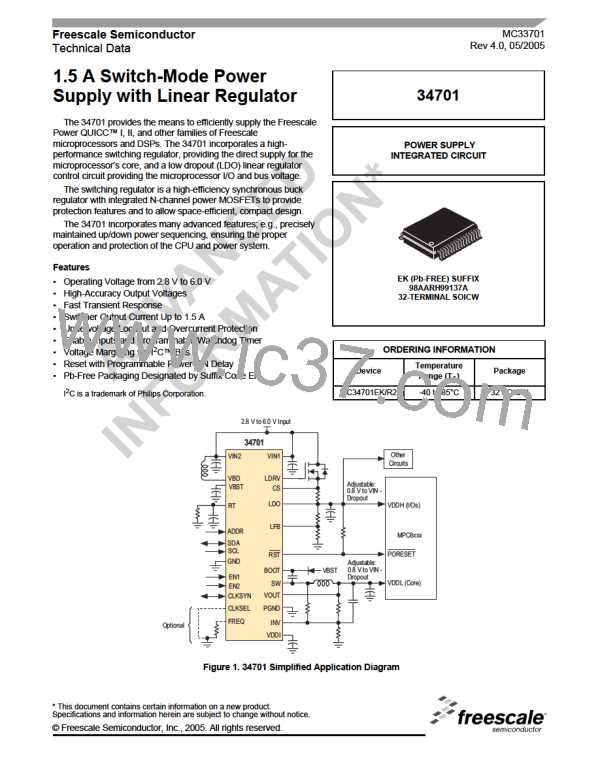
VIN2
The LDO supplies the microprocessor I/O voltage. The
switcher supplies the core (e.g., 1.5 V nominal) (see
Figure 18, page 22).
In the case VIN1 = VIN2, the intrinsic operation turns
on both the Buck High-Side MOSFET and the LDO
external Pass MOSFET, and discharges the LDO load
capacitor into the VIN supply.
Power-Up
2. LDO falls faster than VOUT. The switcher uses control
methods (5) and (6) described in the section Methods
of Control on page 22.
This condition depends upon the regulator current limit,
load current and capacitance, and the relative rise times of
the VIN1 and VIN2 supplies. There are two cases:
1. LDO rises faster than VOUT. The LDO uses control
methods (1) and (2) described in the section Methods
of Control on page 22.
Shorted Load
1. VOUT shorted to ground. The LDO uses method (1)
and (2) described in the section Methods of Control on
page 22.
2. VOUT rises faster than LDO. The switcher uses control
methods (5) and (6) described in the section Methods
of Control on page 22.
2. LDO shorted to ground. The switcher uses control
methods (5) and (6) described in the section Methods
of Control on page 22.
Power-Down
3. VIN1 shorted to ground. Device is not working.
This condition depends upon the regulator load current
and capacitance and the relative fall times of the VIN1 and
VIN2 supplies. There are two cases:
4. VIN2 shorted to ground with VIN1 and VIN2 different.
This is equivalent to the switcher output shorted to
ground.
5. VOUT shorted to supply. No load protection. 34701 is
protected by current limit and Thermal Shutdown.
6. LDO shorted to supply. No load protection. 34701 is
protected by current limit and Thermal Shutdown.
34701
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor
24
 FREESCALE [ Freescale ]
FREESCALE [ Freescale ]