MVTX2801
Data Sheet
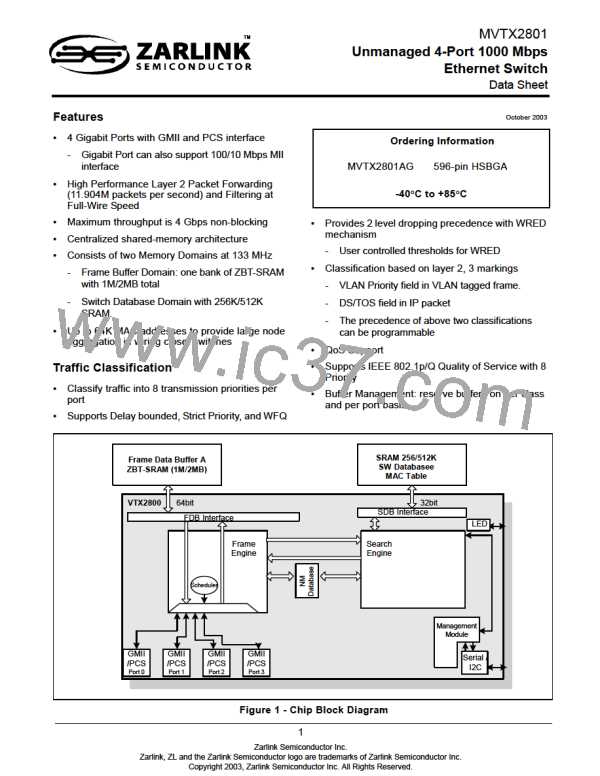
1.0 Block Functionality
1.1 Frame Data Buffer (FDB) Interfaces
The FDB interface supports pipelined ZBT-SRAM memory at 133 MHz. To ensure a non-blocking switch, one
memory domain is required. Each domain has a 64-bit wide memory bus. At 133 MHz, the aggregate memory
bandwidth is 8.5 Gbps, which is enough to support 4 Gigabit ports at full wire speed switching. A patent pending
scheme is used to access the FDB memory. Each slot has one tick to read or write 8 bytes.
1.2 Switch Database (SDB) Interface
A pipelined synchronous burst SRAM (SBRAM) memory is used to store the switch database information including
MAC Table. Search Engine accesses the switch database via SDB interface. The SDB bus has 32-bit wide bus at
133MHz.
1.3 GMII/PCS MAC Module (GMAC)
The GMII/PCS Media Access Control (MAC) module provides the necessary buffers and control interface between
the Frame Engine (FE) and the external physical device (PHY). The MVTX2801 has two interfaces, GMII or PCS.
The MAC of the MVTX2801 meets the IEEE 802.3z specification and supports the MII interface. It is able to operate
10M/100M/1G in Full Duplex mode with a back pressure/flow control mechanism. It has the options to insert Source
Address/CRC/VLAN ID to each frame. The GMII/PCS Module also supports hot plug detection.
1.4 Frame Engine
The main function of the frame engine is to forward a frame to its proper destination port or ports. When a frame
arrives, the frame engine parses the frame header (64 bytes) and formulates a switching request, which is sent to
the search engine to resolve the destination port. The arriving frame is moved to the FDB. After receiving a switch
response from the search engine, the frame engine performs transmission scheduling based on the frame's priority.
The frame engine forwards the frame to the MAC module when the frame is ready to be sent.
1.5 Search Engine
The Search Engine resolves the frame's destination port or ports according to the destination MAC address (L2) by
searching the database. It also performs MAC learning, priority assignment, and trunking functions.
1.6 LED Interface
The LED interface can be operated in a serial mode or a parallel mode. In the serial mode, the LED interface uses
3 pins for carrying 4 port status signals. In the parallel mode, the interface can drive LEDs by 8 status pins. The LED
port is shared with bootstrap pins. In order to avoid error when reading the bootstraps, a buffer must be used to
isolate the LED circuitry from the bootstrap pins during bootstrap cycle (the bootstrap pins are sampled at the rising
edge of the Reset).
1.7 Internal Memory
Several internal tables are required and are described as follows:
•
•
Frame Control Block (FCB) - Each FCB entry contains the control information of the associated frame stored
in the FDB, e.g. frame size, read/write pointer, transmission priority, etc.
MCT Link Table - The MCT Link Table stores the linked list of MCT entries that have collisions in the external
MAC Table.
10
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
 ZARLINK [ ZARLINK SEMICONDUCTOR INC ]
ZARLINK [ ZARLINK SEMICONDUCTOR INC ]