UCD9090
SLVSA30A –APRIL 2011–REVISED AUGUST 2011
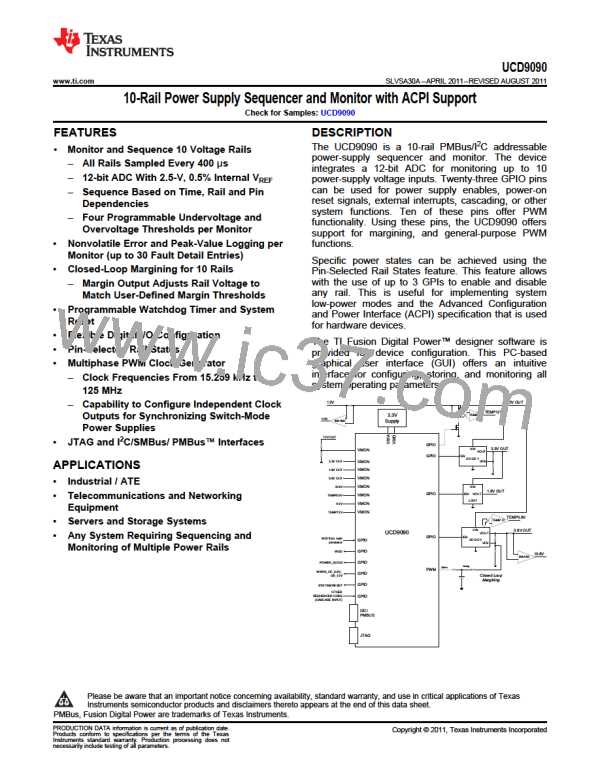
www.ti.com
After the pins have been configured, other key monitoring and sequencing criteria are selected for each rail from
the Vout Config tab (Figure 5):
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Nominal operating voltage (Vout)
Undervoltage (UV) and overvoltage (OV) warning and fault limits
Margin-low and margin-high values
Power-good on and power-good off limits
PMBus or pin-based sequencing control (On/Off Config)
Rails and GPIs for Sequence On dependencies
Rails and GPIs for Sequence Off dependencies
Turn-on and turn-off delay timing
Maximum time allowed for a rail to reach POWER_GOOD_ON or POWER_GOOD_OFF after being enabled
or disabled
•
Other rails to turn off in case of a fault on a rail (fault-shutdown slaves)
Figure 5. Fusion GUI VOUT-Config Tab
The Synchronize margins/limits/PG to Vout checkbox is an easy way to change the nominal operating voltage
of a rail and also update all of the other limits associated with that rail according to the percentages shown to the
right of each entry.
The plot in the upper left section of Figure 5 shows a simulation of the overall sequence-on and sequence-off
configuration, including the nominal voltage, the turnon and turnoff delay times, the power-good on and
power-good off voltages and any timing dependencies between the rails.
After a rail voltage has reached its POWER_GOOD_ON voltage and is considered to be in regulation, it is
compared against two UV and two OV thresholds in order to determine if a warning or fault limit has been
exceeded. If a fault is detected, the UCD9090 responds based on a variety of flexible, user-configured options.
Faults can cause rails to restart, shut down immediately, sequence off using turnoff delay times or shut down a
group of rails and sequence them back on. Different types of faults can result in different responses.
10
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]
TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]