ISL83080E, ISL83082E, ISL83083E, ISL83085E, ISL83086E, ISL83088E
Test Circuits and Waveforms (Continued)
+1.5V
-1.5V
RE
15pF
A
0V
0V
B
0V
RO
R
A
t
t
PHL
PLH
V
CC
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
1.5V
1.5V
RO
0V
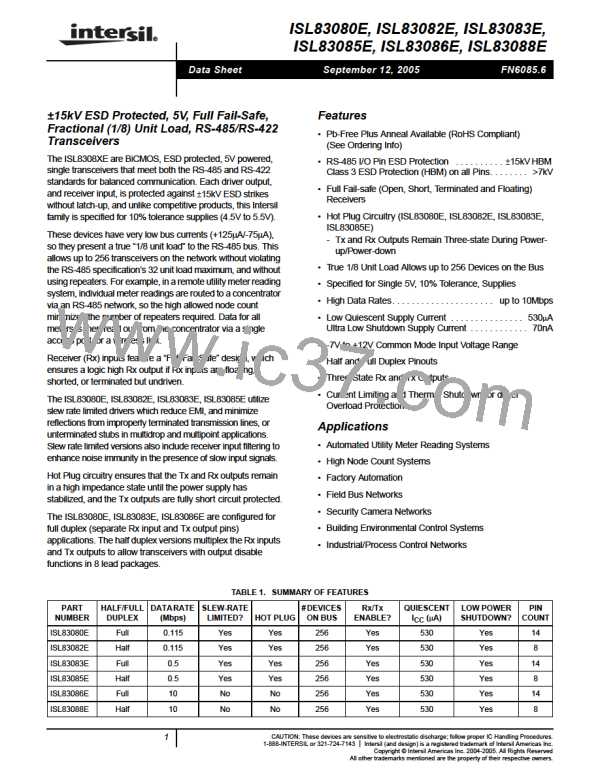
FIGURE 5A. TEST CIRCUIT
FIGURE 5B. MEASUREMENT POINTS
FIGURE 5. RECEIVER PROPAGATION DELAY AND DATA RATE
RE
NOTE 9
B
A
3V
0V
1kΩ
V
GND
CC
RO
RE
R
1.5V
1.5V
HZ
GND
SW
SIGNAL
15pF
GENERATOR
t
, t
ZH ZH(SHDN)
t
NOTE 9
OUTPUT HIGH
1.5V
V
OH
V
- 0.5V
OH
PARAMETER
DE
0
A
SW
RO
0V
t
+1.5V
-1.5V
+1.5V
-1.5V
+1.5V
-1.5V
GND
HZ
t
, t
t
0
V
ZL ZL(SHDN)
t
LZ
LZ
CC
NOTE 9
V
CC
t
(Note 8)
(Note 8)
0
GND
ZH
RO
1.5V
t
0
V
ZL
CC
V
+ 0.5V
OL
V
OL
OUTPUT LOW
t
(Note 11)
(Note 11)
0
GND
ZH(SHDN)
t
0
V
CC
ZL(SHDN)
FIGURE 6A. TEST CIRCUIT
FIGURE 6B. MEASUREMENT POINTS
FIGURE 6. RECEIVER ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES
Receiver Features
Application Information
These devices utilize a differential input receiver for maximum
noise immunity and common mode rejection. Input sensitivity
is ±200mV, as required by the RS-422 and RS-485
specifications.
RS-485 and RS-422 are differential (balanced) data
transmission standards for use in long haul or noisy
environments. RS-422 is a subset of RS-485, so RS-485
transceivers are also RS-422 compliant. RS-422 is a point-
to-multipoint (multidrop) standard, which allows only one
driver and up to 10 (assuming one unit load devices)
receivers on each bus. RS-485 is a true multipoint standard,
which allows up to 32 one unit load devices (any
combination of drivers and receivers) on each bus. To allow
for multipoint operation, the RS-485 spec requires that
drivers must handle bus contention without sustaining any
damage.
Receiver input resistance of 96kΩ surpasses the RS-422
spec of 4kΩ, and is eight times the RS-485 “Unit Load (UL)”
requirement of 12kΩ minimum. Thus, these products are
known as “one-eighth UL” transceivers, and there can be up
to 256 of these devices on a network while still complying
with the RS-485 loading spec.
Receiver inputs function with common mode voltages as
great as ±7V outside the power supplies (i.e., +12V and
-7V), making them ideal for long networks where induced
voltages are a realistic concern.
Another important advantage of RS-485 is the extended
common mode range (CMR), which specifies that the driver
outputs and receiver inputs withstand signals that range from
+12V to -7V. RS-422 and RS-485 are intended for runs as
long as 4000’, so the wide CMR is necessary to handle
ground potential differences, as well as voltages induced in
the cable by external fields.
All the receivers include a “full fail-safe” function that
guarantees a high level receiver output if the receiver inputs
are unconnected (floating) or shorted.
FN6085.6
10
September 12, 2005
 INTERSIL [ Intersil ]
INTERSIL [ Intersil ]