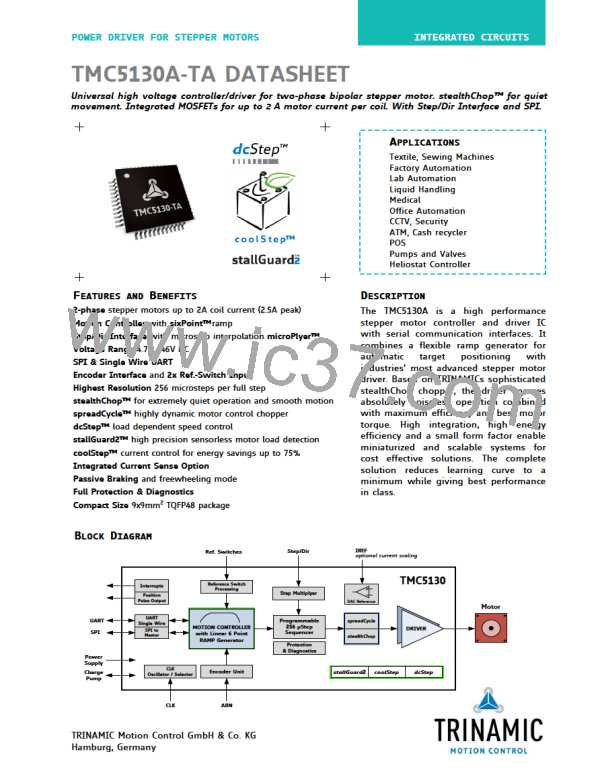
TMC5130A DATASHEET (Rev. 1.14 / 2017-MAY-15)
53
Motor current
PWM scale
Velocity
PWM reaches
max. amplitude
255
RMS current
constant
P
W
M
Nominal current
_
G
(sine wave RMS)
R
k
A
o
D
D
A
o
Current may drop due
to high velocity
R
k
G
_
M
W
P
Stand still
PWM scale
0
0
Time
Setting for PWM_GRAD ok.
Motor current
PWM scale
Velocity
Current overshoots
due to too small
PWM_GRAD
255
Nominal current
(sine wave RMS)
Current drops due to
too small PWM_GRAD
Stand still
PWM scale
0
0
Time
Setting for PWM_GRAD slightly too small.
Figure 7.4 Good and too small setting for PWM_GRAD
Be sure to use a symmetrical sense resistor layout and sense resistor traces of identical length and
well matching sense resistors for best performance.
Quick Start
For a quick start, see the Quick Configuration Guide in chapter 24.
7.2.1 Lower Current Limit
The stealthChop current regulator imposes a lower limit for motor current regulation. As the coil
current can be measured in the shunt resistor during chopper on phase only, a minimum chopper
duty cycle allowing coil current regulation is given by the blank time as set by TBL and by the
chopper frequency setting. Therefore, the motor specific minimum coil current in stealthChop
autoscaling mode rises with the supply voltage and with the chopper frequency. A lower blanking
time allows a lower current limit. Extremely low currents (e.g. for standstill power down) can be
realized with the non-automatic current scaling or with the freewheeling option, only. The run current
setting needs to be kept above the lower limit: In case the PWM_SCALE drops to a too low value, e.g.
because the current scale was too low, the regulator may not be able to recover. The regulator will
recover once the motor is in standstill. The freewheeling option allows going to zero motor current.
The lower motor coil current limit can be calculated from motor parameters and chopper settings:
www.trinamic.com
 TRINAMIC [ TRINAMIC MOTION CONTROL GMBH & CO. KG. ]
TRINAMIC [ TRINAMIC MOTION CONTROL GMBH & CO. KG. ]