TPS736xx
www.ti.com
SBVS038K–SEPTEMBER 2003–REVISED SEPTEMBER 2005
APPLICATION INFORMATION
The TPS736xx belongs to a family of new generation
LDO regulators that use an NMOS pass transistor to
achieve ultra-low-dropout performance, reverse cur-
rent blockage, and freedom from output capacitor
constraints. These features, combined with low noise
and an enable input, make the TPS736xx ideal for
portable applications. This regulator family offers a
wide selection of fixed output voltage versions and an
adjustable output version. All versions have thermal
and over-current protection, including foldback cur-
rent limit.
Input and Output Capacitor Requirements
Although an input capacitor is not required for stab-
ility, it is good analog design practice to connect a
0.1µF to 1µF low ESR capacitor across the input
supply near the regulator. This will counteract reac-
tive input sources and improves transient response,
noise rejection, and ripple rejection. A higher-value
capacitor may be necessary if large, fast rise-time
load transients are anticipated or the device is lo-
cated several inches from the power source.
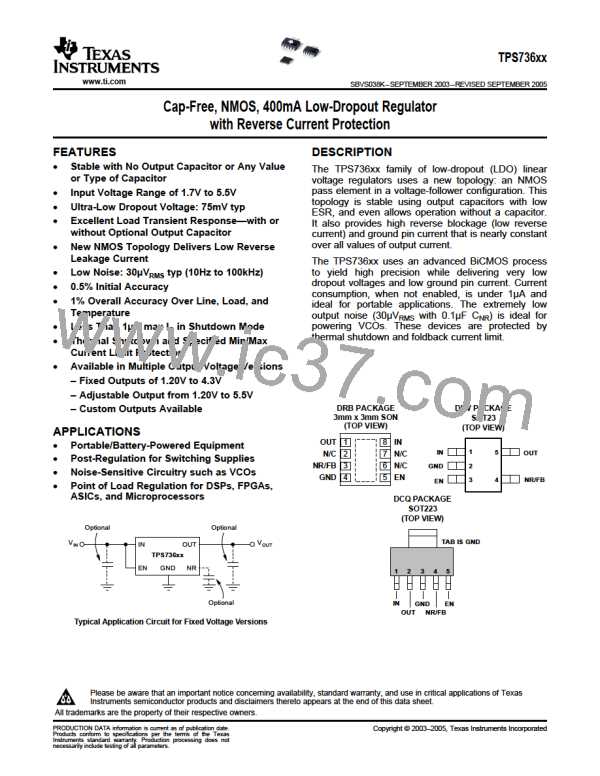
Figure 31 shows the basic circuit connections for the
fixed voltage models. Figure 32 gives the connections
for the adjustable output version (TPS73601). R1 and
R2 can be calculated for any output voltage using the
formula in Figure 32. Sample resistor values for
common output voltages are shown in Figure 2. For
best accuracy, make the parallel combination of R1
and R2 approximately 19kΩ.
The TPS736xx does not require an output capacitor
for stability and has maximum phase margin with no
capacitor. It is designed to be stable for all available
types and values of capacitors. In applications where
VIN – VOUT < 0.5V and multiple low ESR capacitors
are in parallel, ringing may occur when the product of
COUT and total ESR drops below 50nΩF. Total ESR
includes all parasitic resistances, including capacitor
ESR and board, socket, and solder joint resistance.
In most applications, the sum of capacitor ESR and
trace resistance will meet this requirement.
Optional input capacitor.
May improve source
Optional output capacitor.
May improve load transient,
noise, or PSRR.
impedance, noise, or PSRR.
Output Noise
VIN
VOUT
IN
OUT
TPS736xx
GND
A precision band-gap reference is used to generate
the internal reference voltage, VREF. This reference is
the dominant noise source within the TPS736xx and
it generates approximately 32µVRMS (10Hz to
100kHz) at the reference output (NR). The regulator
control loop gains up the reference noise with the
same gain as the reference voltage, so that the noise
voltage of the regulator is approximately given by:
EN
NR
Optional bypass
capacitor to reduce
output noise.
Figure 31. Typical Application Circuit for
Fixed-Voltage Versions
VOUT
VREF
(R1 ) R2)
VN + 32mVRMS
+ 32mVRMS
R2
(1)
Optional input capacitor.
May improve source
impedance, noise, or PSRR.
Optional output capacitor.
May improve load transient,
noise, or PSRR.
Since the value of VREF is 1.2V, this relationship
reduces to:
mVRMS
V
ǒ Ǔ
VN(mVRMS) + 27
VOUT(V)
VIN
VOUT
IN
OUT
FB
(2)
TPS736xx
R1
R2
CFB
for the case of no CNR
.
EN
GND
An internal 27kΩ resistor in series with the noise
reduction pin (NR) forms a low-pass filter for the
voltage reference when an external noise reduction
capacitor, CNR, is connected from NR to ground. For
CNR = 10nF, the total noise in the 10Hz to 100kHz
bandwidth is reduced by a factor of ~3.2, giving the
approximate relationship:
Optional capacitor
reduces output noise
and improves
(R1 + R2)
×
1.204
VOUT
=
R1
transient response.
Figure 32. Typical Application Circuit for
Adjustable-Voltage Versions
mVRMS
ǒ Ǔ
VN(mVRMS) + 8.5
VOUT(V)
V
(3)
for CNR = 10nF.
11
 TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]
TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]