TAS5614LA
SLAS846 –MAY 2012
www.ti.com
Table 5. Fault Handling
Fault/Event
Description
Global or
Channel
Reporting
Method
Latched/Self
Clearing
Fault/Event
Action needed to Clear
Output FETs
PVDD_X UVP
VDD UVP
Increase affected supply
voltage
Voltage Fault
Global
FAULT Pin
Self Clearing
Hi-Z
GVDD_X UVP
AVDD UVP
Power On
Reset
POR (DVDD UVP)
BST UVP
Global
FAULT Pin
None
Self Clearing
Self Clearing
Self Clearing
Latched
Allow DVDD to rise
H-Z
HighSide Off
Normal operation
Hi-Z
Allow BST cap to recharge
(low side on, VDD 12V)
Channel (half
bridge)
Voltage Fault
Thermal
Warning
Cool below lower OTW
threshold
OTW
Global
Global
OTW Pin
FAULT Pin
Thermal
Shutdown
OTE (OTSD)
Toggle RESET
OLP (CBC >2.6ms)
OC shutdown
OC shutdown
Channel
Channel
FAULT Pin
FAULT Pin
Latched
Latched
Toggle RESET
Toggle RESET
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Latched OC (ROC >47k)
reduce signal level or
remove short
Flip state, cycle by
cycle at fs/2
CBC (24k<ROC<33k)
OC Limiting
No PWM
Channel
Channel
Global
None
None
None
Self Clearing
Self Clearing
Self Clearing
Stuck at Fault(1) (1 to 3
channels)
Stuck at Fault(2) (All
channels)
resume PWM
resume PWM
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
No PWM
(1) Stuck at Fault occurs when input PWM drops below minimum PWM frame rate given in Recommended Operating Conditions.
(2) Stuck at Fault occurs when input PWM drops below minimum PWM frame rate given in Recommended Operating Conditions.
DEVICE RESET
When RESET is asserted low, all power-stage FETs in the four half-bridges are forced into a high-impedance
(Hi-Z) state.
In BTL modes, to accommodate bootstrap charging prior to switching start, asserting the reset input low enables
weak pulldown of the half-bridge outputs. In the SE mode, the output is forced into a high impedance state when
asserting the reset input low. Asserting reset input low removes any fault information to be signaled on the
FAULT output, i.e., FAULT is forced high. A rising-edge transition on reset input allows the device to resume
operation after an overload fault. To ensure thermal reliability, the rising edge of RESET must occur no sooner
than 4 ms after the falling edge of FAULT.
SYSTEM DESIGN CONSIDERATION
A rising-edge transition on reset input allows the device to execute the startup sequence and starts switching.
Apply audio only according to the timing information for startup and shutdown sequence. That will start and stop
the amplifier without audible artifacts in the output transducers.
The CLIP signal indicates that the output is approaching clipping (when output PWM starts skipping pulses due
to loop filter saturation). The signal can be used to initiate an audio volume decrease or to adjust the power
supply rail.
The device inverts the audio signal from input to output.
The DVDD and AVDD pins are not recommended to be used as a voltage source for external circuitry.
18
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TAS5614LA
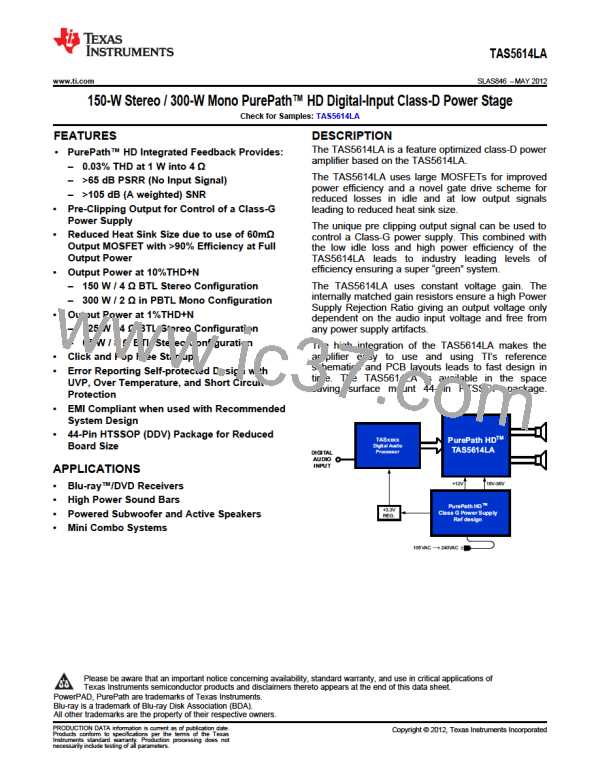
 TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]
TI [ TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ]