APPLICATION NOTES
REGULATOR PROTECTION:
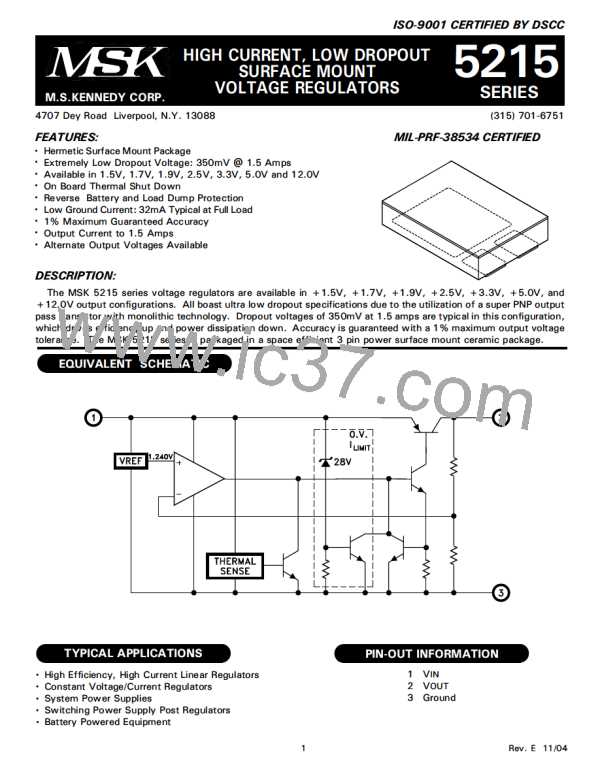
PACKAGE CONNECTIONS:
The MSK 5215 series is fully protected against re-
versed input polarity, overcurrent faults, overtemperature
conditions (Pd) and transient voltage spikes of up to 60V.
If the regulator is used in dual supply systems where the
load is returned to a negative supply, the output voltage
must be diode clamped to ground.
The MSK 5215 series are highly thermally conductive
devices and the thermal path from the package heat sink
to the internal junctions is very short. Standard surface
mount soldering techniques should be used when mount-
ing the device. Some applications may require additional
heat sinking of the device.
HEAT SINK SELECTION:
OUTPUT CAPACITOR:
The output voltage ripple of the MSK 5215 series volt-
age regulators can be minimized by placing a filter ca-
pacitor from the output to ground. The optimum value
for this capacitor may vary from one application to the
next, but a minimum of 33µF is recommended for opti-
mum performance. Transient load response can also be
improved by placing a capacitor directly across the load.
The capacitor should not be an ultra-low ESR type. Tan-
talum capacitors are best for fast load transients but
aluminum electrolytics will work fine in most applica-
tions.
To select a heat sink for the MSK 5215, the following
formula for convective heat flow may be used.
Governing Equation:
Tj = Pd x (Rθjc + Rθcs + Rθsa) + Ta
WHERE:
Tj = Junction Temperature
Pd = Total Power Dissipation
Rθjc = Junction to Case Thermal Resistance
Rθcs = Case to Heat Sink Thermal Resistance
Rθsa = Heat Sink to Ambient Thermal Resistance
Ta = Ambient Temperature
LOAD CONNECTIONS:
In voltage regulator applications where very large load
currents are present, the load connection is very impor-
tant. The path connecting the output of the regulator to
the load must be extremely low impedance to avoid af-
fecting the load regulation specifications. Any imped-
ance in this path will form a voltage divider with the load.
First, the power dissipation must be calculated as fol-
lows:
Power Dissipation = (Vin - Vout) x Iout
Next, the user must select a maximum junction tem-
perature. The absolute maximum allowable junction tem-
perature is 125°C. The equation may now be rearranged
to solve for the required heat sink to ambient thermal
resistance (Rθsa).
MINIMIZING POWER DISSIPATION:
Many applications can not take full advantage of the
extremely low dropout specifications of the regulator due
to large input to output voltage differences. The simple
circuit below illustrates a method to reduce the input
voltage at the regulator to just over the dropout specifi-
cation to keep the internal power dissipation minimized:
EXAMPLE:
An MSK 5215-3.3 is configured for Vin=+5V and
Vout=+3.3V. Iout is a continuous 1A DC level. The
ambient temperature is +25°C. The maximum desired
junction temperature is 125°C.
Rθjc = 3.5°C/W and Rθcs = 0.5°C/W typically.
Power Dissipation = (5V - 3.3V) x (1A)
= 1.7 Watts
Solve for Rθsa:
Rθsa = 125°C - 25°C - 3.5°C/W - 0.5°C/W
1.7W
[
= 54.82°C/W
]
For a given continuous maximum load of 1 amp, R1
can be selected to drop the voltage seen at the regulator
to 4V. This allows for the output tolerance and dropout
specifications. Input voltage variations (5V) also should
be included in the calculations. The resistor should be
sized according to the power levels required for the ap-
plication.
In this example, a heat sink with a thermal resistance
of no more than 54°C/W must be used to maintain a
junction temperature of no more than 125°C.
3
Rev. E 11/04
 MSK [ M.S. KENNEDY CORPORATION ]
MSK [ M.S. KENNEDY CORPORATION ]