AD8240
ADVANTAGES OF DRIVING LED LAMPS WITH CONSTANT VOLTAGE
The advantages of driving LED lamps with constant voltage are
DRIVING AUTOMOTIVE LEDS
There are two different architectures for driving LEDs in
left/right/center brake lamps, running lamps, and turn signals.
•
•
•
Low system cost
Accurate monitoring
Proven strategy
Constant Current
The most common method for driving LEDs is with a constant
current. This current can be supplied from a constant current
source or from a constant voltage source in series with a ballast
resistor. Driving LEDs without some form of ballast carries
some risk of premature LED failure due to thermal runaway in
high temperature ambient conditions.
BACKGROUND
A great variety of LED lamps are being used in automotive
applications. The most popular application is center brake
lamps. Currently, many manufacturers are developing
technology to use LEDs for left/right brake lamps, running
lamps, and turn signals. There are also plans to use high power
LEDs for forward lighting fog lamps and low beams.
For example, in the simplest application, the center brake lamp
is driven from a relatively constant voltage with brightness
controlled by a series ballast resistor. This simple driving
method has been used in a wide variety of automotive platforms
for some time. With this method, the LEDs and ballast resistors
are preselected for brightness as part of the manufacturing
strategy.
There are two fundamental types of LEDs used in these applica-
tions. The first is the low power bright LED. The second type is
the high power, extremely bright LED in the 1 W to 10 W range.
While the following information can be applied to applications
using the high power LED, or incandescent lamps, the constant
voltage method is designed for applications typically using the
low power bright LEDs. This type of LED is used in arrays that
form LED lamps.
When driving with a constant current source, LED driving
and monitoring cannot be done using two or fewer wires
(shared ground). Since the current is constant, it does not
change with partial LED failure. Instead, the current is divided
among the remaining functional LEDs, causing them to fail
prematurely at an unpredictable rate. Additionally, it is not
possible to detect partial failure by measuring the voltage
change. The voltage does not change by a detectable amount
because of the steep V/I curve exhibited by bright LEDs. When
using a constant current scheme, at least one additional wire
per lamp must be added to the harness to monitor partial or
total LED failure. Additionally, electronic modules must be
added to each lamp.
MONITORING THE LEDS
In addition to driving the LED lamp, the electronics in the
control module must include a method for monitoring partial
LED failure in the lamp. Certain factors, such as overdriving
and mechanical stress, can cause LED failures.
Auto manufacturers are using LED lamps as a way to differen-
tiate themselves and give a car a unique appearance. Several
failed LEDs in the lamp would ruin the aesthetics of the lamp.
As a result, manufacturers are demanding the ability to monitor
the LED lamps for partial failure.
Constant Voltage
Driving LEDs with a constant voltage allows for easy, low cost
detection of partial failure, an advantage not available with a
constant-current architecture. This is because the current from
the voltage source changes in direct proportion to the number
of LEDs that have failed. This current can be measured with a
low cost shunt and an amplifier back at the body control
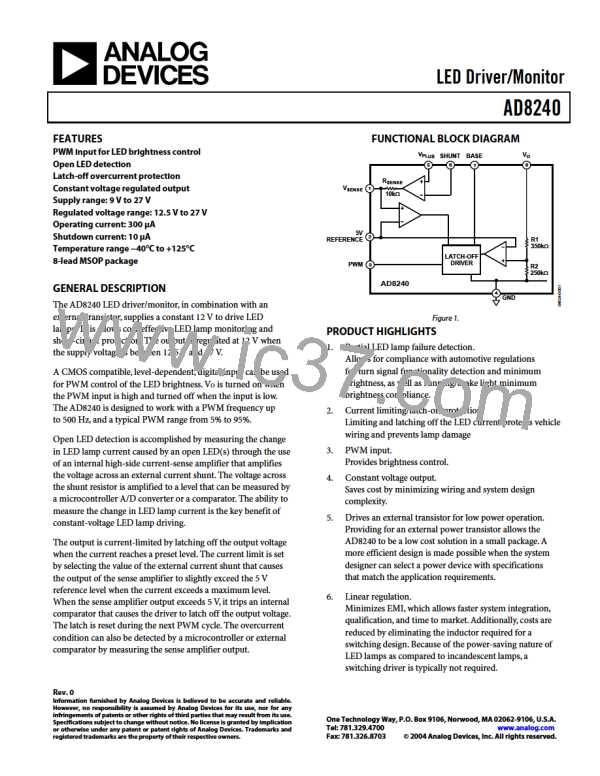
module. This detection scheme is implemented in the AD8240
LED driver/monitor through the use of a high-side, current-
sensing amplifier. The current is measured on the high side in
order to separate the current from those combined in the
chassis ground return or shared-wire ground return.
In addition to monitoring the LEDs for aesthetic reasons,
monitoring must also be included as a result of automotive
regulations. These regulations specify the minimum light
output of external lamps. For example, if half of the LEDs in
a particular lamp failed, the lamp would still operate, but the
light output would be insufficient to meet automotive
regulations for brightness. This concern is not an issue for
incandescent bulbs, because they are either completely on or
completely off. The ability of the LED lamp to provide some
light output in the case of partial outage, however, allows for an
extra degree of safety over incandescent lamps. Additionally,
there are automotive regulations requiring the monitoring of
the turn signals regardless of the type of light source.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 12
 ADI [ ADI ]
ADI [ ADI ]